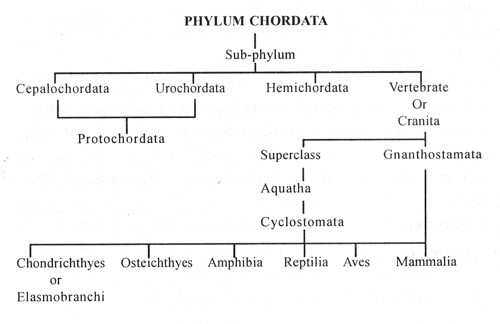
The sub-phylum vertebrata is divided into live classes;
(a) Fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
Fishes are aquatic vertebrates with fins as locomotor organs and gills as respiratory ones; cold-blooded, i.e., body temperature varies with the ambient. Body is streamlined; ten pairs of cranial nerves present; skin covered with scales; heart is two chambered and contains only deoxygenated blood; red blood cells are nucleated.
There are two subclasses—
- Cartilaginous fishes as sharks, sting ray, and saw fish; and
- bony fishes as seahorse.
(b) Amphibians lead a double life, living equally well on land and water; cold blooded with two pairs of limbs (the caecilians Are without' limbs and the sirens have only the hind limbs. They are mostly oviparous and their development often involves metamorphoses, involving an intermediate larval form. Examples: frogs, toads, salamander and newts.
(c) Reptiles are cold blooded air breathing vertebrates which have adapted themselves completely to land. Some, however, have secondarily taken to water; normally two pair of short limbs with claws, but in some, they are reduced, modified or lost (as paddles in turtles, lost in snakes). There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves; most are oviparous, snakes are viviparous, no metamorphosis.
Examples: turtles and tortoises, (former are aquatic); lizards (garden, wall, flying); chameleons; snakes—cobra, krait, and vipers are the common poisonous snakes; rat snake and pythons are non-poisonous snakes; crocodiles and alligators.
(d) Birds are warm-blooded, adapted to aerial life; streamlined body covered with feathers; fore limbs are modified as wings for flight, hind limbs are used for perching, walking or swimming; some are incapable of flight (running birds—ostrich and kiwi. Flying birds are—pigeons,, ducks (aquatic), parrots, kites, owls (nocturnal).
(e) Mammals the highest group in animal kingdom; warm-blooded and terrestrials, a few have become secondarily aquatic and some have become aerial; have many glands (sweat, scent) including the mammary glands in females which secrete milk for nourishing the young; ears have external pinna, eyes have eyelids; heart is 4-chamber; respiration is by lungs only; Cerebral hemispheres are well developed reaching their maximum in human beings; male has a copulatory organ—the penis; fertilization is internal, the embryo is connected to the wall of the uterus by the placenta and are viviparous. Examples: rabbits, rats, bats, squirrels, guinea pigs, cattle, horses; cats—lions, tigers; dogs—wolf, foxes; elephants, giraffes, dolphins, whales, etc. and humans.
 Jethalal S. Zaveri
Jethalal S. Zaveri
 Prof. Muni Mahendra Kumar
Prof. Muni Mahendra Kumar

