The third type of RNA in the cell is ribosomal RNA, it constitutes about 60% of the ribosome. The remainder of the ribosome is protein, containing about 75 different types of proteins that are both structural proteins and enzymes needed in the manufacturer of protein molecules.
The ribosome is the physical structure in the cytoplasm on which protein molecules are actually synthesized. However it always function in association with both the other type of RNA as well, transfer RNA transports amino acids to the ribosomes for incorporation into the developing protein molecule, where as messenger RNA provides the information necessary for sequencing the amino acids in proper order for each specific type of protein to be manufactured.
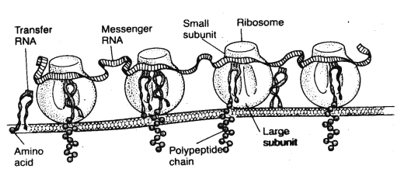
The ribosomes of nucleated cells are composed of two physical subunits, called the small sub unit, containing one RNA molecule and 33 proteins and the large sub units containing 30 RNAs and more than 40 proteins. Although we have only partial knowledge of the mechanism of protein manufacture in the ribosome, it is known that messenger RNA and transfer RNA first complex with the small sub unit. Then the large sub unit provide most of the enzymes that promote peptide linkage between the successive amino acid. Thus the ribosome act as a manufacturing plant in which the protein molecules are formed.
Fig.34:
An artist's concept of the physical structures of the ribosomes as well as their functional relationship to messenger RNA, transfer RNA and the endoplasmic reticulum during the formation of protein molecules.
The ribosome is simply the structure in which the chemical reactions take place for manufacture of proteins. As illustrated in figure 33 while the messenger RNA travels along the ribosome, a protein molecule is formed - a process called "translation". Thus, the ribosome reads the code of the messenger RNA in much the same way that a tape is "read" as it passes through the play back head of a tape recorder. Then when a "stop" (or chain terminating) codon slips past the ribosome, the end of a protein molecule is signaled, and the protein molecule is freed into the cytoplasm. Figure 34 shows the functional relationship of messenger RNA to the ribosomes and also the manner in which the ribosomes attach to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Note the process of translation occurring in several ribosomes at the same time in response to the some strand of messenger RNA. Note also the newly forming polypeptide chains passing through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane into the endoplasmic matrix.
Yet it should be noted that except in glandular cells that form large amounts of protein - containing secretary vesicles, most proteins, formed by the ribosomes are released directly to the cytosol. These are enzymes and the internal structural proteins of the cell.
 Prof. Dr. Sohan Raj Tater
Prof. Dr. Sohan Raj Tater
 Doctoral Thesis, JVBU
Doctoral Thesis, JVBU