Transport of both oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place either as a solute or in combination with other compounds.
Oxygen transport - oxygenated blood having P02of 100 mmHg contains only about 0.3 ml of dissolved 02 per 100 ml of blood. It combines with the haemoglobin in 100 ml of blood which can unite with 1.34 ml of oxygen. The exact amount of oxygen in blood depends mainly on the amount of haemoglobin. The heme portion of haemoglobin contains four atoms of iron, each capable of binding to a molecule of O2 Oxygen and haemoglobin binds in an easily reversible reaction to form oxyhemoglobin

About 98% of oxygen that is bound to haemoglobin is trapped inside RBC. Thus only the dissolved oxygen (about 1.5%) can diffuse out of tissue capillaries into tissue cells.
Carbon dioxide transport - Normally each 100 ml of deoxygenated blood contains the equivalent of 35 ml of gaseous C02, which is transported in the blood in three main forms.
- Dissolved C02 - A little amount (about 7%) is dissolved in blood plasma. After reaching the lungs, it diffuses into alveolar air and is exhaled.
- Carbamino compound - A larger amount (about 23%), combines with the amino group of amino acids and proteins in blood to form carbamino compounds. Prominent protein in blood is haemoglobin, most of the C02 to be transported is bounded to haemoglobin. The main C02 binding takes place at terminal amino acids. Haemoglobin that bind with C02 is termed as Carbaminohemoglobin (Hb-CO2)

The formation of Hb-CO2 is greatly affected by PC02
- Bicarbonate ions - The higher percentage of C02, (about 70%), is transported in blood plasma as bicarbonate ions (HC03-). As C02 diffuse into systemic capillaries and enters RBCs, it reacts with water in the presence of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA) to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into H+ and HCO
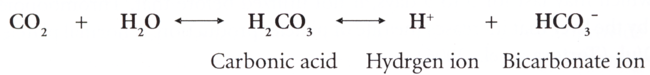
Thus, as blood picks up CO2, HC03- accumulates inside RBCs. Some HC03- moves out into the blood plasma. Because of Chloride shift phenomenon net effect is that C02 is removed from tissue cells and transported in blood plasma as HC03-. As blood passes through pulmonary capillaries in the lungs, all these reactions reverse and C02 is exhaled (Thibodeau, 1999).
The amount of C02 that can be transported in the blood is influenced by the percent saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen. The lower the amount of oxyhemoglobin (Hb-O2), the higher the C02 carrying capacity of the blood, a relationship known as the Haldane effect.
 Prof. J.P.N. Mishra
Prof. J.P.N. Mishra
